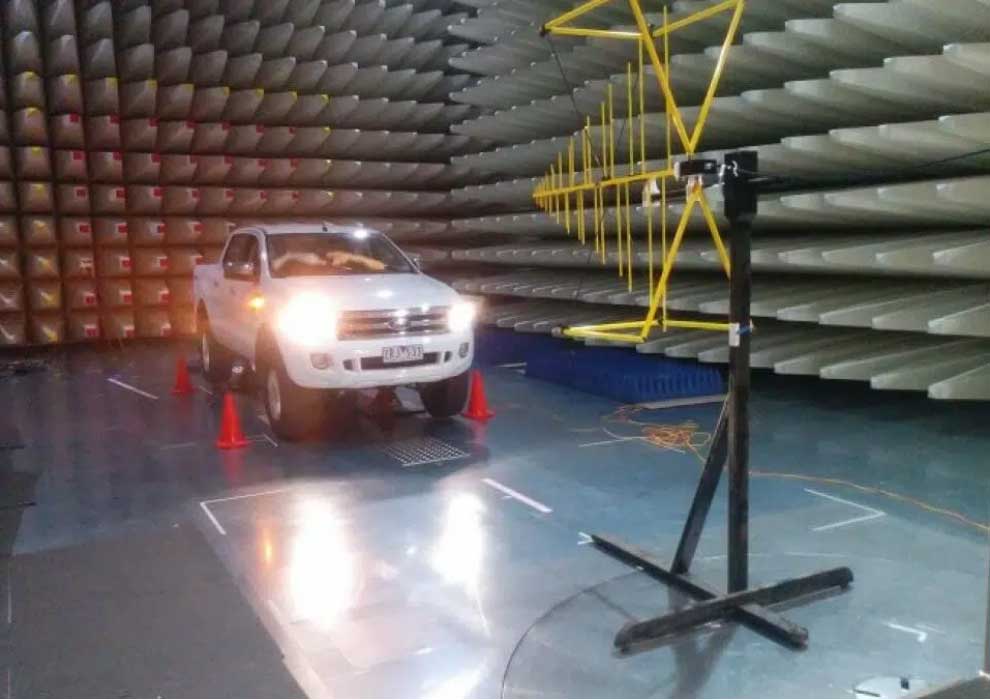

WHAT IS ECE R10?
ECE R10 is one of the regulations published by The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) for automotive industry. UNECE has 56 member states as of 18 February 2020. ECE R10 is defining Electromagnetic Compatibility requirements of the vehicles and electronic sub assemblies (ESAs) used in automotive. It explains both EMC tests and type approval of the product.
WHICH PRODUCTS ARE UNDER THE SCOPE OF ECE R10?
As given on the scope of ECE R10, the regulation applies to:
1.1. Vehicles of categories L, M, N O, T, R and S1 with regard to electromagnetic compatibility;
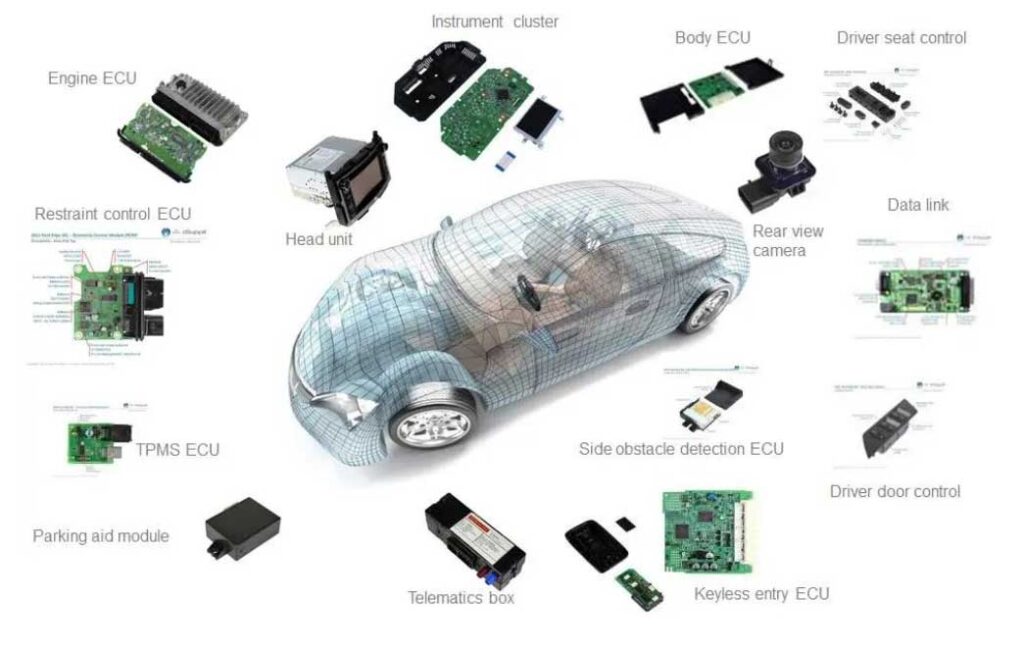
1.2. Components and separate technical units intended to be fitted in these vehicles with the limitation given in paragraph 3.2.1. with regard to electromagnetic compatibility.
1.3. It covers: (a) Requirements regarding the immunity to radiated and conducted disturbances for functions related to direct control of the vehicle, related to driver, passenger and other road users’ protection, related to disturbances, which would cause confusion to the driver or other road users, related to vehicle data bus functionality, related to disturbances, which would affect vehicle statutory data; (b) Requirements regarding the control of unwanted radiated and conducted emissions to protect the intended use of electrical or electronic equipment at own or adjacent vehicles or nearby, and the control of disturbances from accessories that may be retrofitted to the vehicle; (c) Additional requirements for vehicles and ESAs providing coupling systems for charging the REESS regarding the control of emissions and immunity from this connection between vehicle and power grid.
WHICH VERSIONS OF ECE R10 ARE PUBLISHED?
Version of ECE R10 is mentioned as ECE R10 Rev.6, ECE R10 Rev.5 or ECE R10 Rev.4. The latest version is Revision 6 and it has been officially published by UN ECE. On 30 October 2020, United Nations published an amendment for ECE R10 Rev.6. ECE R10 regulations and its amendments are free documents, you can download them by visiting official website of UN ECE. However, you can not reach test standards mentioned in the regulation since most of the test standards are not free of charge. If you need to check the details of standards you have to purchase them from web store of the standard publisher. Alternatively, you can ask Testups any technical questions about the tests.
WHAT ARE THE OTHER REGULATIONS PUBLISHED BY UN ECE?
ECE R10 is not the only regulation published by UN ECE. There are 160 regulations published by UN ECE. Each regulation specify requirements of the different types of vehicles or components that will be used on that vehicles.
DIFFERENT LANGUAGE VERSIONS OF ECE R10
There are three language options for ECE R10 regulation published by The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). You can click below links to reach English, French or Russian.
ECE R10 Rev 6 English
ECE R10 Rev 6 French
ECE R10 Rev 6 Russian
ECE R10 Rev 6 Deutsch is not available. However, you can get some general information about ECE regulations in German by clicking here.
ECE R10 TESTING
UN ECE R10 explains how to perform EMC tests and there are various test standards that are applied. Each test and test setup is explained in detail. UN ECE R10 EMC Tests can be categorized into two groups: emission and immunity. Emission and immunity tests are performed according to referred test standards. The standards referred to UN ECE R10 Revision 6 are listed below:
CISPR 12, CISPR 16-1-4, CISPR 25, ISO 7637-2, ISO-EN 17025, ISO 11451, ISO 11451-1, ISO 11451-2, ISO 11451-4, ISO 11452, ISO 11452-1, ISO 11452-2, ISO 11452-3, ISO 11452-4, ISO 11452-5, ITU Radio Regulations, edition 2008, IEC 61000-3-2, IEC 61000-3-3, IEC 61000-3-11, IEC 61000-3-12, IEC 61000-4-4, IEC 61000-4-5, IEC 61000-6-3, CISPR 16–2–1, CISPR 22, CISPR 16-1-2, IEC 61851-1 and CISPR 32.
What are immunity related functions?
ECE R10 mentions immunity related functions of the vehicle. This defines the test plan since products with immunity related functions need much more testing. “Immunity related functions” are listed as six function categories. This list is not exhaustive and shall be adapted to the technical evolution of vehicle or technology.
1) Functions related to the direct control of the vehicle:
- By degradation or change in: e.g. engine, gear, brake, suspension, active steering, speed limitation devices;
- By affecting drivers position: e.g. seat or steering wheel positioning;
- By affecting driver’s visibility: e.g. dipped beam, windscreen wiper, indirect vision systems, blind spot systems.
2) Functions related to driver, passenger and other road user protection:
- E.g. airbag and safety restraint systems, emergency calling systems;
3) Functions which, when disturbed, cause confusion to the driver or other road users:
- Optical disturbances: incorrect operation of e.g. direction indicators, stop lamps, end outline marker lamps, rear position lamp, light bars for emergency system, wrong information from warning indicators, lamps or displays related to functions in subparagraphs (a) or (b) which might be observed in the direct view of the driver;
- Acoustical disturbances: incorrect operation of e.g. anti-theft alarm, horn.
4) Functions related to vehicle data bus functionality:
- By blocking data transmission on vehicle data bus-systems, which are used to transmit data, required to ensure the correct functioning of other immunity related functions.
5) Functions which when disturbed affect vehicle statutory data: e.g. tachograph, odometer;
6) Function related to charging mode when coupled to the power grid:
- For vehicle test: by leading to unexpected vehicle motion;
- For ESA test: by leading to an incorrect charging condition (e.g. over-current, over-voltage).
How to apply ECE R10 tests?
EMC tests are performed according to relevant clauses of ECE R10 regulation at EMC testing laboratories. EMC testing laboratories which are able to perform ECE R10 tests, are equipped with IEC, ISO or CISPR compliant EMC test chambers and equipments. Test experts check the product features and functions and make a test plan according to applicable ECE R10 EMC tests. Emission and immunity tests are performed. As Testups offers, ECE R10 tests can be finished in 4 weeks, if the product passes all product-specific EMC tests listed on the regulation and referred standards. After passing all applicable ECE R10 tests, test report is issued for the product (vehicle or ESA). This test report shows the ECE R10 test results of the product and it is required if the product also needs ”E-mark” or type approval according to UN ECE R10.
ECE R10 TYPE APPROVAL OR HOMOLOGATION
After ECE R10 tests are done and PASS test report issued, Type Approval or Homologation (E-marking) can be also issued for the product. In this step, ECE R10 test report, technical documents of the product and quality documents (like valid ISO 9001 certificate) of the manufacturing or/and distributor company are checked by a third party and authorized agency. They are also called designated technical service. If all product and company documents are submitted properly, E mark including a unique number can be affixed or labeled on the product.
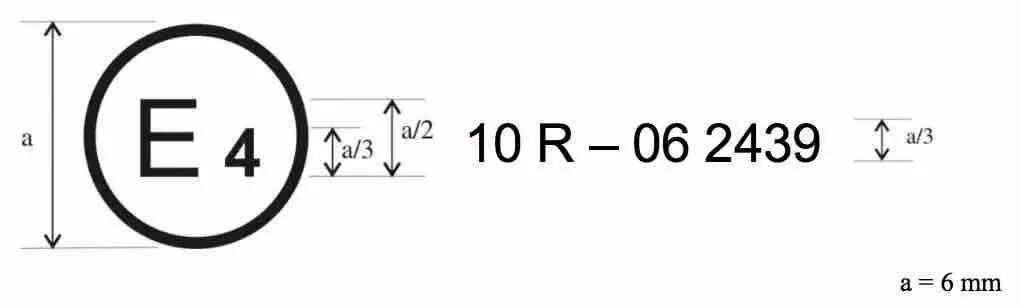
Examples of approval marks
The below approval mark affixed to a vehicle or ESA shows that the vehicle type concerned has, with regard to electromagnetic compatibility, been approved in the Netherlands (E 4) pursuant to Regulation No. 10 under approval No. 05 2439. The approval number indicates that the approval was granted according to the requirements of Regulation No. 10 as amended by the 06 series of amendments.
Which countries are covered by ECE R10?
There are 57 countries which are under the scope of UN ECE Regulation 10. Each country has a ECE symbol and designated type approval authority. For instance for Ireland, ECE symbol is E24 and designated type approval authority is NSAI. For whole list of ECE R10 countries visit this page: ECE R10 Countries
COSTS FOR EMC TESTING AND TYPE APPROVAL
There are two cost item for ECE R10 compliance: testing and type approval.
What are the costs for ECE R10 EMC testing?
EMC testing costs depend on the features of the product, test plan, and location of test laboratory. If your product is a simple electronic sub assembly which has no immunity related function, reduced EMC tests are allowed. This will make costs lower. For such a simple product operating at a single voltage and with a single operation mode, ECE R10 testing costs will change in this range: 2.500 – 3.000 EUR.
What are the costs for ECE R10 Type Approval?
Type approval costs depend on the agency or country issuing the type approval. Although E1(Germany) and E24(Ireland) marks are technically identical, E1 marking takes some much more time and a bit expensive than E24 due to authorized agency costs. ECE R10 type approval (E marking) costs will change in this range: 1.500 – 2.000 EUR.
How to reduce ECE R10 testing costs ?
If you are suffering from the costs for ECE R10 testing and type approval, take into account suggestions listed below:
- Check ECE R10 EMC tests during the design stage of your products. Early testing would save you time and money since you would have opportunity to get test results before serial production.
- Use same or similar electronic components when designing your products. Using similar electronic components would increase the probability of the PASS ratio of test results. If you use various types of electronic components, ensure that they have been EMC tested or certified.
- Group similar products in terms of electromagnetic compatibility and reduce number of model names with product family names. ECE R10 allows product grouping if technically applicable. When defining your product model names, try to group them under a product family model names.
- Start testing with pre-compliance EMC tests during design validation stage of your products, this would save time and cost during ECE R10 certification. If an electronic product or vehicle never tested before, it would probably fail at one of ECE R10 tests. Pre-compliance testing would save you time and money even it seems causing extra costs.
- Try to perform some EMC tests in house by having EMC test equipments (if you regularly need ECE R10 testing or type approval service). Work on investing on some of the EMC test instruments and prepare test setups which are most essential for your product. By in house testing, you would get opportunity to design your product more comfortable and to check your product’s EMC performance during its pilot or serial production.
- Build a UN ECE R10 compliant EMC test laboratory (if you have various products that need ECE R10 testing or type approval service). UN ECE R10 compliant test laborotory needs some expert staff like test engineers and technicians. If your team can handle these laboratory operations, building a new test laboratory would make you much more comfortable in terms of electromagnetic compatibility of your products. If you would like go further, have accreditation or authorisation for your laboratory to show your lab’s independency and satisfy your customers.
Regulation No 10 of the Economic Commission for Europe of the United Nations (UN/ECE) — Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to electromagnetic compatibility
ECE Regulation R10 of the Economic Commission for Europe of the United Nations (UN/ECE), the body responsible for implementing global trade agreements within Europe, addresses electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues and applying to vehicles of categories L, M, N O, T, R and S. The regulation requires manufacturers to gain type approval for all vehicles, electronic sub-assemblies, components and separate technical units.
ECE Regulation R10 covers the requirements regarding the immunity to radiated and conducted disturbances related to direct control of the vehicle, the driver, passenger and other road users’ protection. The regulation addresses disturbances which would cause confusion to the driver or other road users, related to vehicle data bus functionality. ECE Regulation R10 also addresses requirements regarding the control of unwanted radiated and conducted emissions to protect the intended use of electrical or electronic equipment from nearby or adjacent vehicles and the control of disturbances from accessories that may be retrofitted to the vehicle.
